
Detail Viewer Overview
The Detail Viewer is a comprehensive data discovery tool that allows you to explore your DMARC data in a variety of ways and to inform you on how to get your email sources compliant with DMARC.
Data Filtering
One of the most heavily used elements of our application, the Detail Viewer is a powerful, intuitive data filtering resource to help with the work of deploying DMARC, saving you time and resources. We continually improve the Detail Viewer for ease-of-use, performance, and improved results. With the following filtering options, you have a greater ability to identify successes, authentication gaps, sending patterns, and much more.
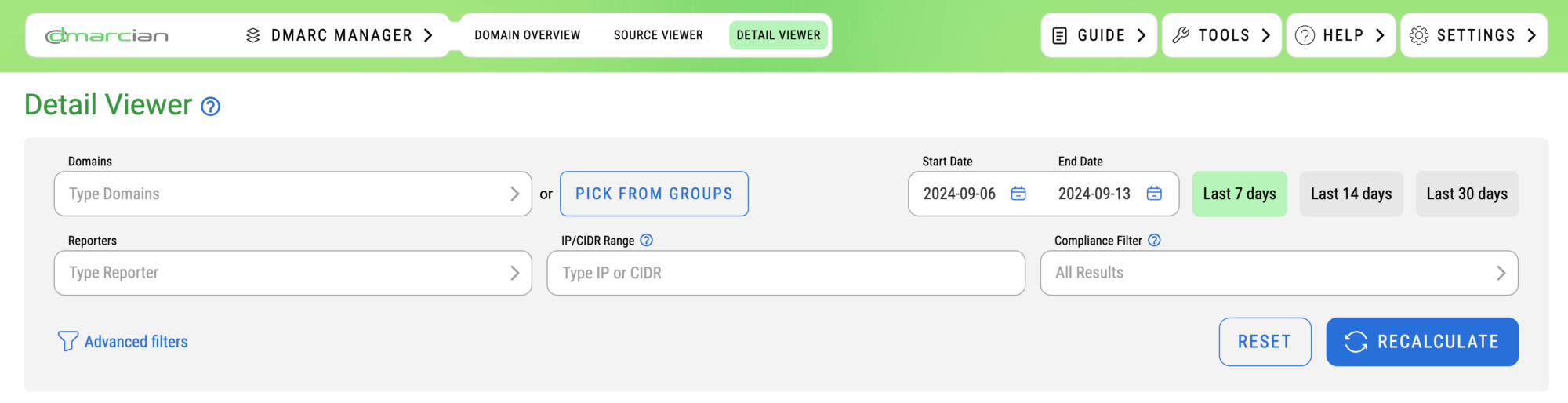
With the basic filtering search parameters, you’re presented with these options:
- Domain: search by a specific domain
- Reporters: search by which source is sending reports
- IP/CIDR: search by IP address or CIDR
- Timeframe: dates for which you’d like to see results
- Compliance Filter
- All results: shows all compliant and non-compliant data
- Show impact of policy: show messages impacted by DMARC policy
- Show non-compliant email: show messages failing DMARC
- Show compliant email: show messages passing DMARC
By enabling the Advanced Filters view, you’ll see the following expanded section:
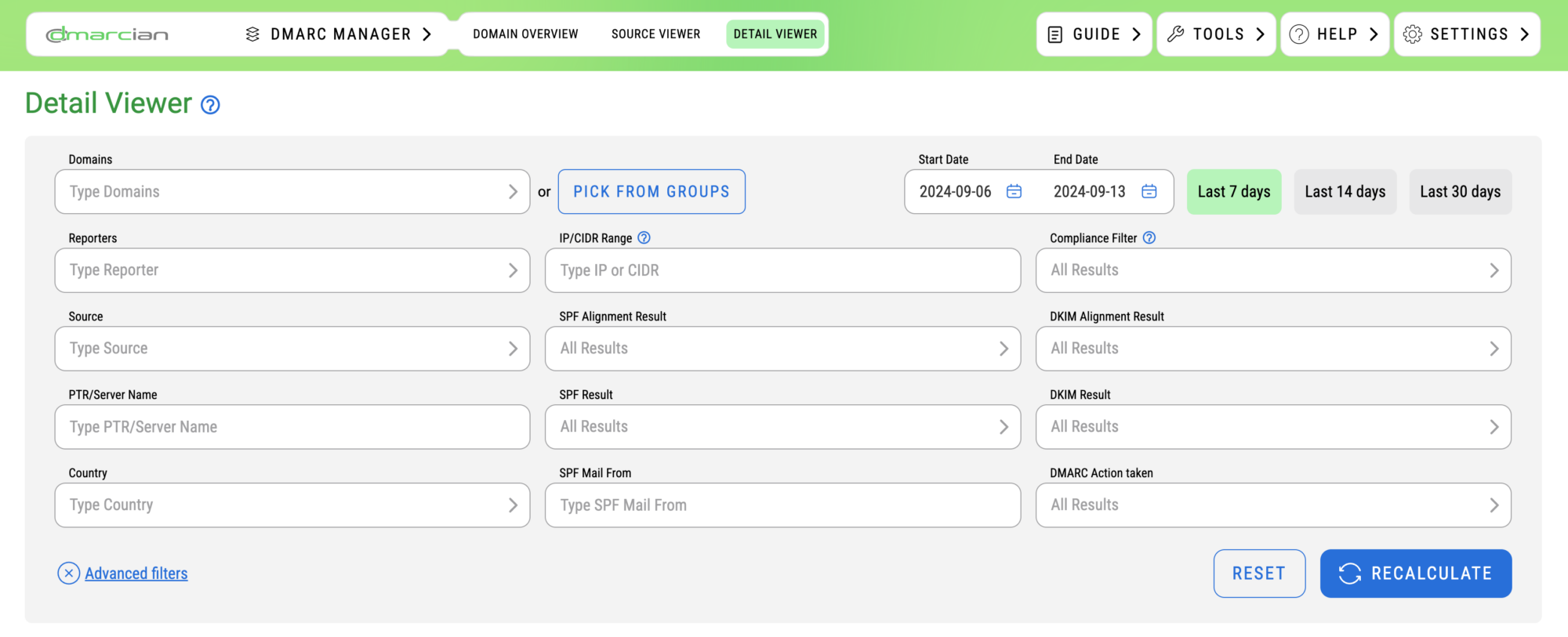
The advanced filters lend both time savings and a means of data exploration necessary for more complex DMARC projects.
Advanced filters include the following fields:
- Source: Isolate a curated list of sources sending on your behalf for management or troubleshooting.
- SPF Alignment Result: Whether or not a particular mail stream meets DMARC compliance requirements by way of SPF.
- DKIM Alignment Result: Whether or not a particular mail stream meets DMARC compliance requirements by way of DKIM.
- PTR/Server Name: The server name of the IP address that transmitted the message (eg. result of DNS PTR lookup on the IP address ).
- SPF Result: The raw SPF check result conducted by the receiver (eg. Did SPF pass/fail/other?).
- DKIM Result: The raw DKIM check result conducted by the receiver (eg. Did DKIM pass/fail/other?).
- Country: The country where the server is believed to be located.
- SPF Mail From: The domain that was used to pass SPF. This field is also referred to as the Envelope-From, bounce domain, and Return-Path.
- DMARC Action Taken: The DMARC policy (if any) that was applied to the message by the recipient email receiver.
In the remainder of this article, we’ll cover the other sections of the Detail Viewer: Email Volume and DMARC Data.
Email Volume by Category
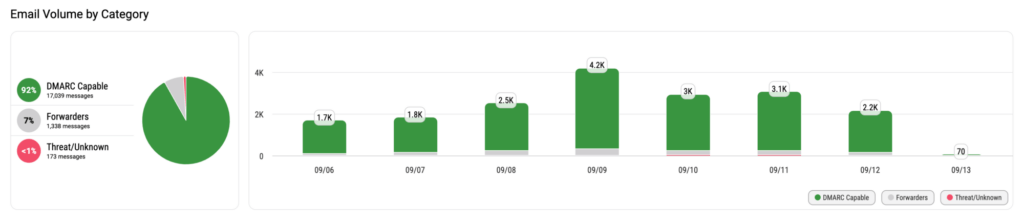
The middle section of the Detail Viewer displays the Email Volume by category. Here, you get a quick look at your email volume and in what categories they fall. Email volume is the number of emails sent from your domain(s). By mousing over images in the platform, you can extract detailed information.
DMARC Data
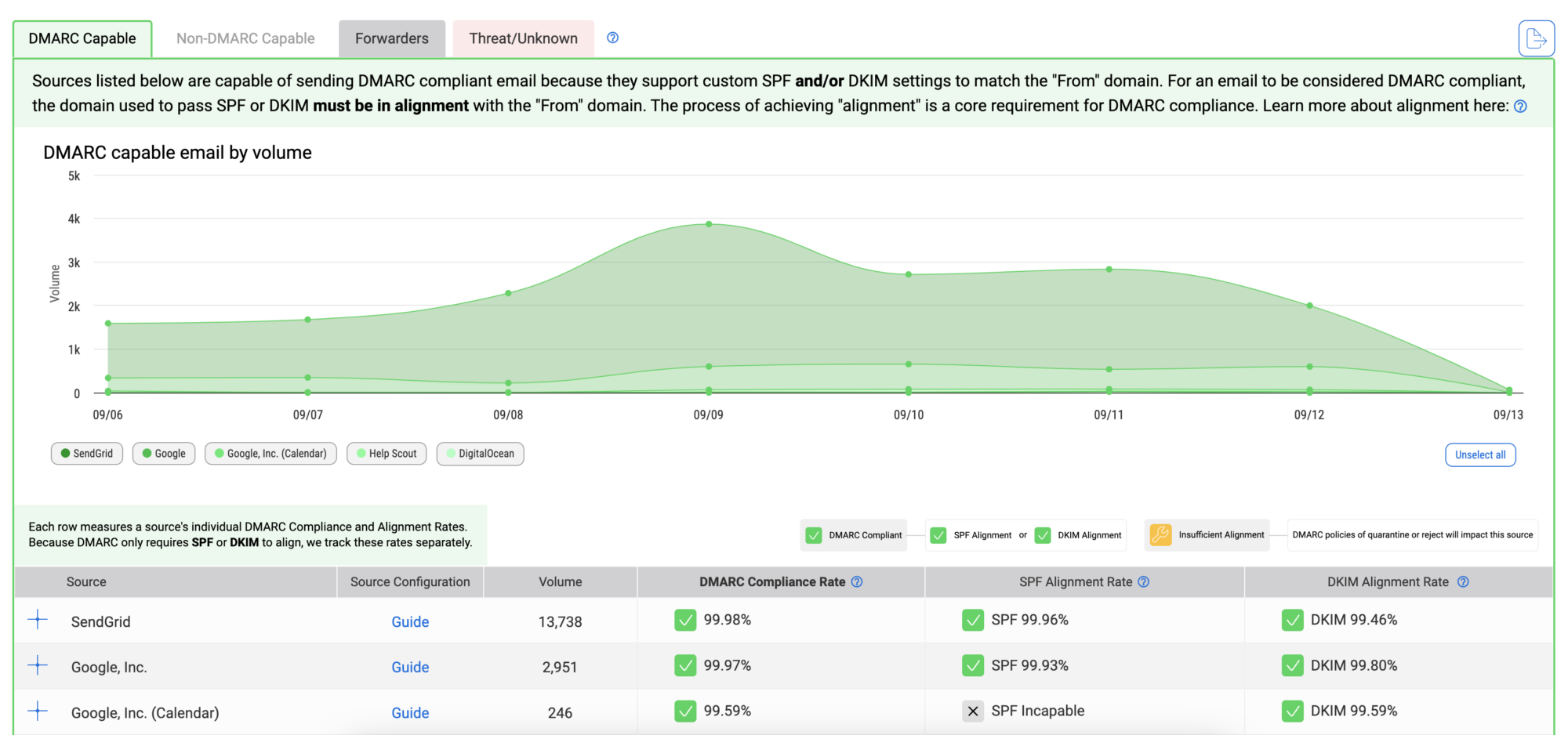
The bottom section of the Detail Viewer shows DMARC data grouped by source.
In this section of the Detail Viewer, you have four navigation tabs that reveal the four high-level categories in which dmarcian classifies DMARC data. The four categories are:
DMARC Capable – a source of email that is capable of sending DMARC-compliant email. When displayed in the dmarcian tools, DMARC-Capable sources are often accompanied by statistics showing the current level of DMARC compliance for email associated with the source. For example, a 25% DMARC compliance rate means that 25% of this source is passing DMARC.
Non-DMARC Capable – a source of email that is not capable of sending DMARC-compliant email. If you’re using a service that shows up in “Non-compliant Sources,” you can refer them to How to send DMARC compliant email on behalf of others.
Forwarders – Forwarding happens when you send an email to [email protected] and John has configured his email to be forwarded to another of his email addresses. Another example of forwarding is how mailing lists route email. From the perspective of the email receiver (the entity that is generating DMARC XML reports), your email appears to be coming out of infrastructure that has nothing to do with you. The Forwarders tab shows which sources are forwarding email on your behalf and whether or not the forwarding is passing DMARC. Forwarded email can only be authenticated via DKIM, though DKIM signatures can be inadvertently broken because of how messages are forwarded through different types of infrastructure. For forwarded email, your DMARC compliance is equal to the “survival” of your DKIM signatures as they travel through forwarders. To increase your DMARC compliance rates, be sure to use DKIM to sign as much mail as is supported by your DMARC-Capable sources. This will allow forwarded messages to pass DMARC checks at the next hop, as long as the intermediary has not changed either the body or significant headers.
Threat/Unknown – Threat/Unknown sources are either fraudulent or need to be identified as legitimate. To help dmarcian identify unknown sources, click the Report as Legitimate button next to the source to provide more information.
When we investigate data to add a source rule, we identify where email is coming from and whether or not the source can be configured for DMARC compliance.
The graph below the navigation tabs provides a chronological visualization of the data category you’ve selected.
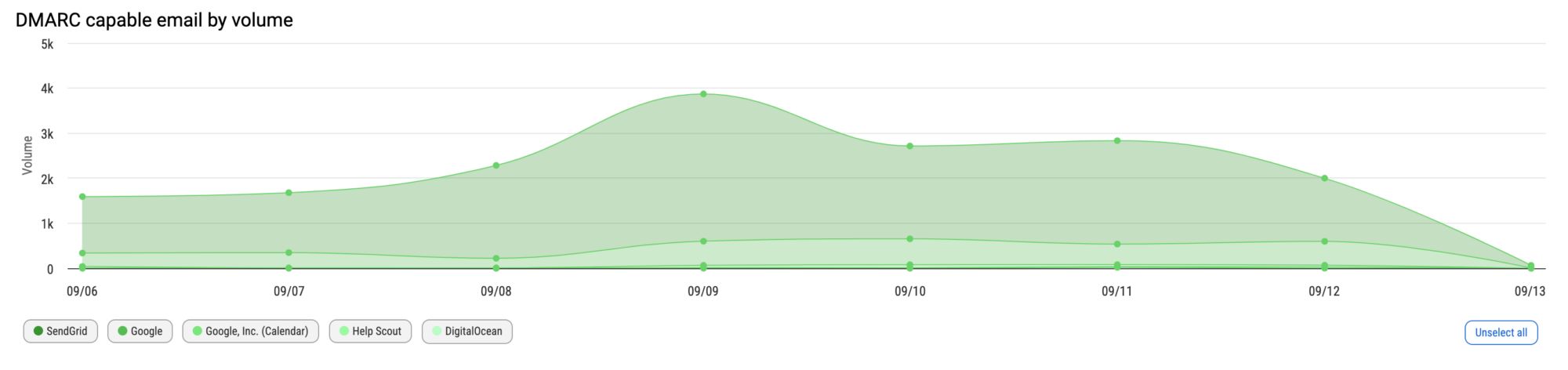
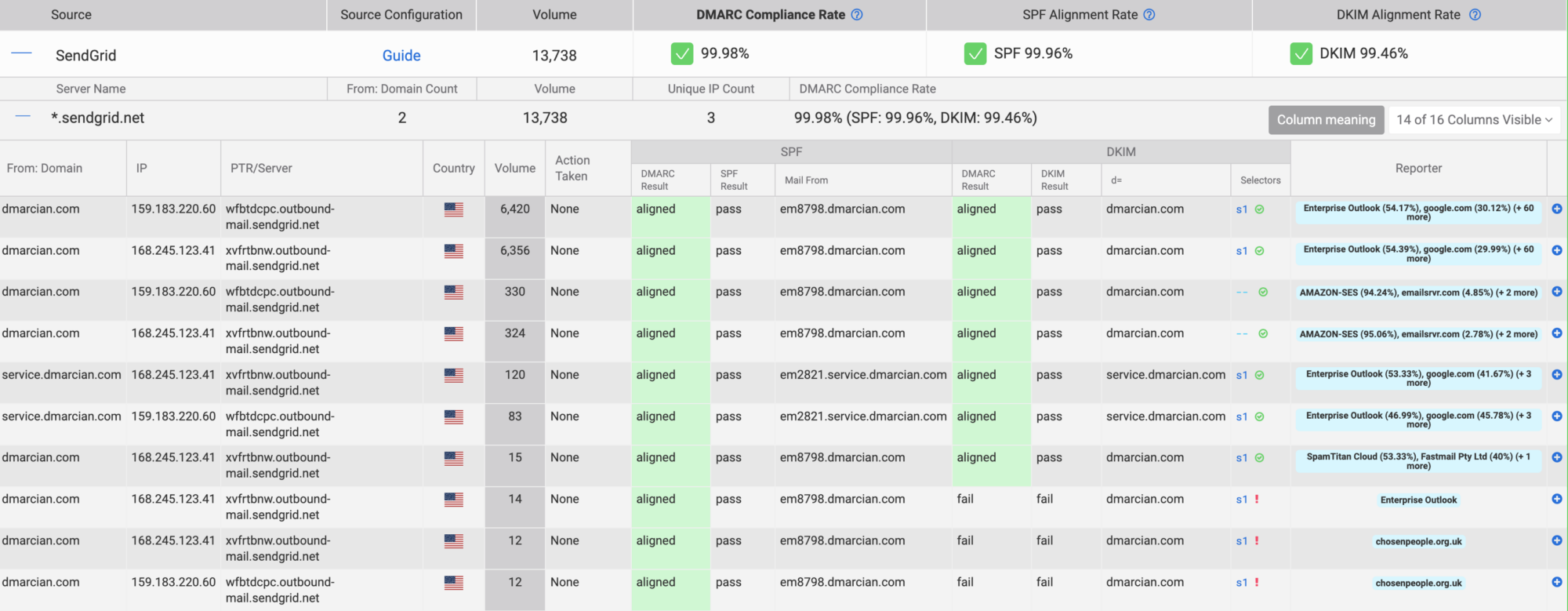
Below this graph, you get a list of your sources and each of these are expandable to reveal the server names and the data columns. You can mouseover the column headers, click on the Column Meanings tab on the right side of the page, or read the article in our knowledge base to learn about the headers and how they relate to your DMARC report.
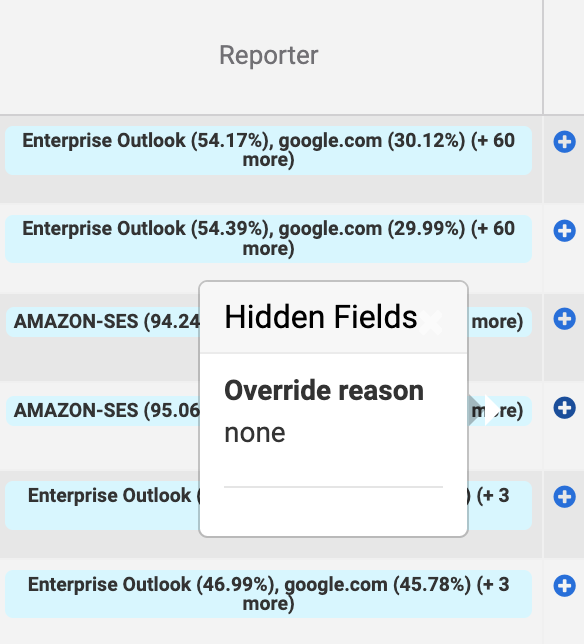
When you click on a reporter in the Reporter column, there is helpful sorting that appears in a popover as well as a new column which shows data in columns you have hidden when you mouse over the blue plus symbol (see below). This is helpful if you’d like quick insight into a particular row, without having to adjust your preferred column visibility options.
The data provided in the Detail Viewer represents your current levels of DMARC compliance, gaps, and the underlying SPF and DKIM values in play on mail flow. You’ll want to have a solid grasp of alignment and how messages achieve a state of DMARC compliance. Interpreting the data can seem challenging at first, but once you’ve understood each of the columns’ meanings and how to filter data, you’ll be on your way.
We’re here to help people understand and deploy DMARC, so get in touch with us if you have any questions about the Detail Viewer.
Want to continue the conversation? Head over to the dmarcian Forum


