How Email Forwarding Affects DMARC
Email forwarding can sometimes throw a wrench in DMARC authentication results, and we often get questions about how to manage forwarded emails, especially with mailing lists.
Emails are forwarded automatically all the time, more so than most people expect. Forwarding happens automatically when you send an email to [email protected] and that person has set up their email to be forwarded to a separate inbox, like [email protected].
Another common instance of automatic forwarding is a mailing list, like Google Groups. From the perspective of the email receiver—the one that is generating DMARC XML reports—your email appears to be coming from an infrastructure that has nothing to do with you.
In Google Groups, DMARC data that displays forwarding will show your domain as a sender, a Google IP as the sender, and a variety of receivers who send the DMARC report as part of their DMARC check. This number can increase quite dramatically if the forwarding is done as part of Google Group delivery. Google Groups behave the same way as mailing lists.
DKIM signing can survive forwarding. If your domain is covered with DKIM, dmarcian’s ability to detect forwarding increases. SPF does not work in the context of forwarding because SPF is simply a list of servers that are authorized to send on behalf of your domain, and it’s not feasible to maintain a list of forwarders in an SPF record. dmarcian supports a set of rules to identify well-known forwarders in our platform to help people identify and analyze forwarded email traffic.
The Forwarders tab in our Detail Viewer below shows which sources are forwarding email on your behalf and whether or not the forwarding is passing DMARC. As we mentioned earlier, forwarded email can only be authenticated by DKIM, though DKIM signatures can be inadvertently broken because of how messages are forwarded through different types of email infrastructure. For forwarded email, your DMARC compliance is equal to the “survival” of your DKIM signatures as they travel through forwarders.
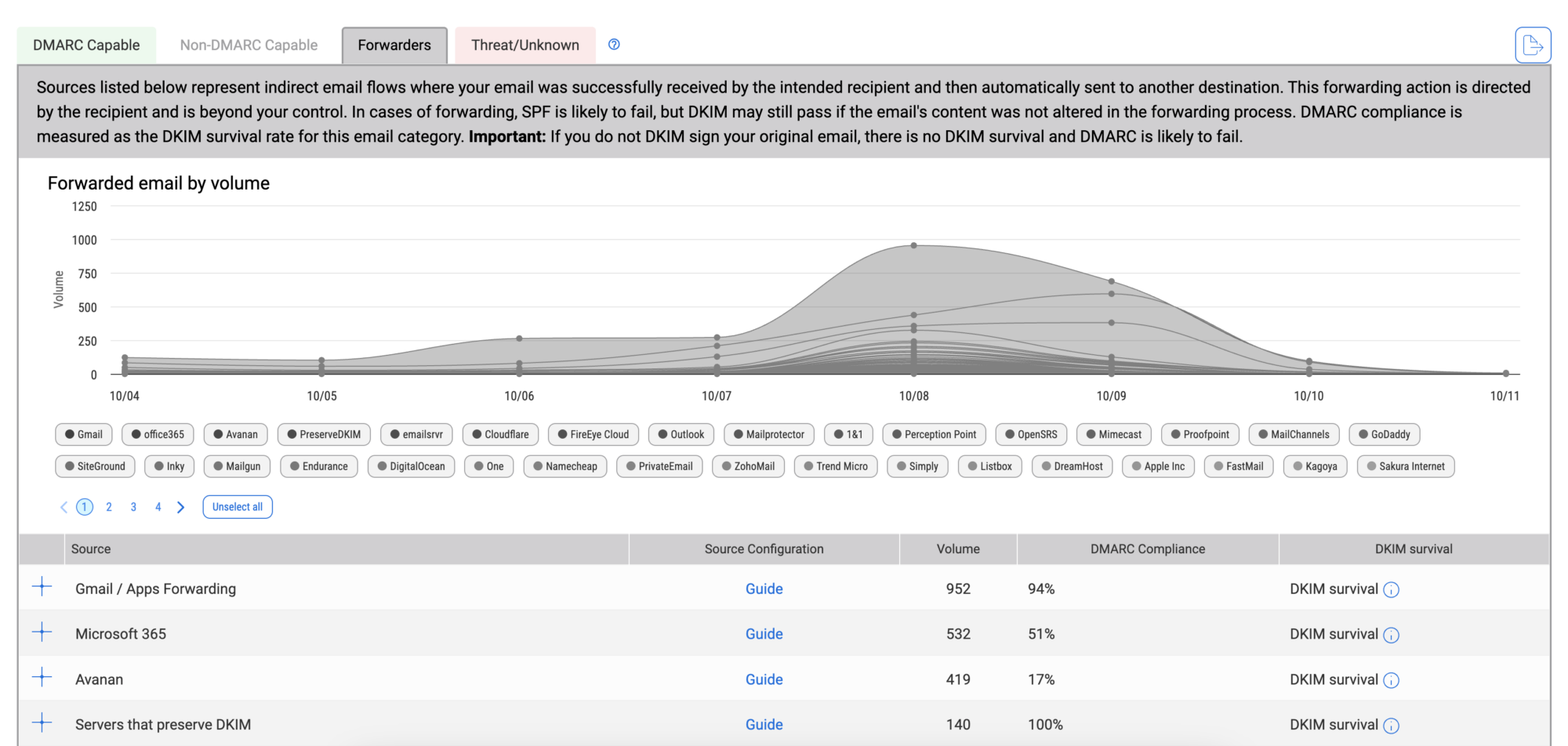
Overall, our Forwarders tab is meant to show you how much and how often the email you send is typically forwarded and their DMARC compliance. To help this compliance, deploy DKIM wherever possible on your email sources.
Asher Morin, dmarcian Director of Deployment
To help operators keep track of email sources’ forwarding capacity, we maintain a directory that lists DMARC-related email forwarders and their DMARC interoperability at https://dmarc.io/forwarders/.
To increase your DMARC compliance rates with forwarding, be sure to use DKIM signing with your DMARC-capable sources that support DKIM. Doing so will allow forwarded messages to pass DMARC checks at the next hop, as long as the intermediary has not changed either the body or relevant headers.
It’s also important to keep in mind that as a domain owner, you have no control over when and where receivers set an automatic forwarding rule for emails received from you. They will become aware in case of failures due to forwarding, and it is their responsibility to take corrective actions in order to successfully receive your emails.
We’re Here to Help
With a team of email security experts and a mission of making email and the internet more trustworthy through domain security, dmarcian is here to help assess an organization’s domain catalog and implement and manage DMARC for the long haul.
Want to continue the conversation? Head over to the dmarcian Forum.